Hey, Let’s Make Code Easier to Read!
Ever looked at decompiled code and groaned at names like var_18 or var_1c? They’re about as helpful as a map with no labels. That’s where AI swoops in to save the day, helping us rename variables to something that actually makes sense. In this post, I’ll walk you through how I used AI to spruce up variable names in a Binary Ninja plugin, making code analysis a breeze.
Step 1: Letting AI Pick Better Names
First up, I let AI take a crack at understanding the code. By feeding it decompiled functions, the AI figures out what each variable is doing. For example, it might spot a variable acting as a loop boundary and suggest calling it digit_lower_bound instead of var_18. It’s like having a super-smart buddy who reads the code and says, “Hey, this variable’s clearly keeping track of the upper limit, let’s name it digit_upper_bound!”

Step 2: Grabbing the Code and Getting AI’s Input
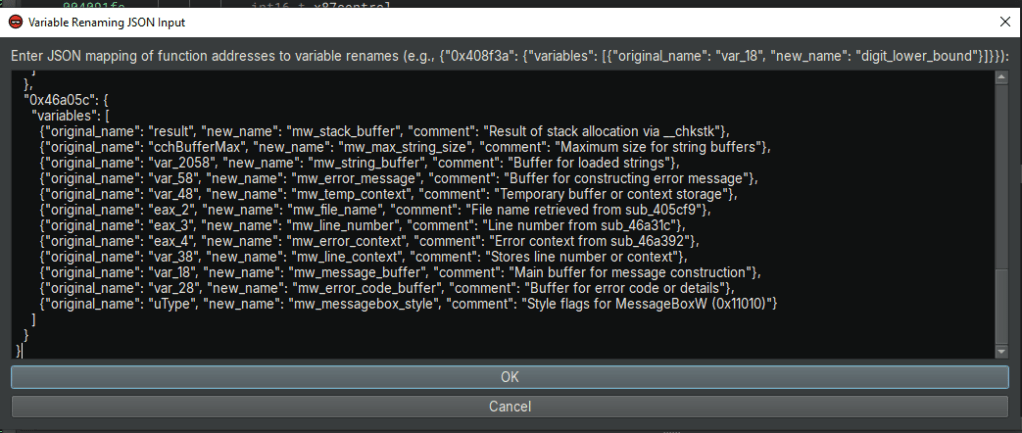
Next, I gather the code and hand it over to the AI for analysis. I’m working with a Python script that’s a Binary Ninja plugin, designed to rename variables based on a JSON file. The AI checks out the code’s structure and variable usage, then spits out a JSON map linking function addresses to new variable names. Here’s what that JSON looks like:

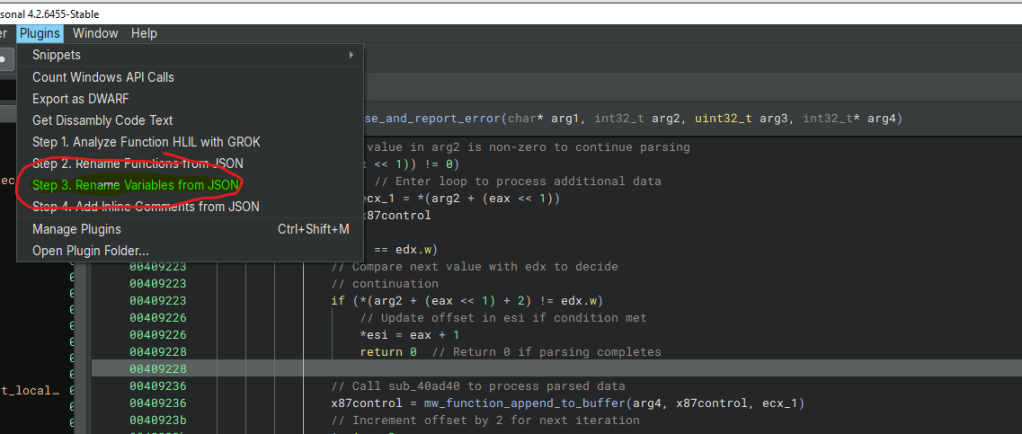
Step 3: Putting AI’s Suggestions to Work
Now comes the fun part: applying those new names! The Binary Ninja plugin pops up a slick Qt dialog where I paste the AI’s JSON. The script reads it, finds the right functions and variables, and swaps out the old names for the new ones. It’s got solid error handling, so if something’s off—like a variable that doesn’t exist, it logs the issue and keeps going. At the end, it gives me a quick rundown of how many names got updated.
Diving Into the Code
The Python script I’m using is a Binary Ninja plugin that makes this renaming magic happen. Let’s break down what it does and how it plays nice with AI suggestions.
from binaryninja import PluginCommand, BinaryView, log_info, log_error, log_debug
from binaryninjaui import UIContext
import json
try:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QDialog, QVBoxLayout, QTextEdit, QPushButton, QLabel
except ImportError:
log_info("Error: PySide6.QtWidgets not available. Please ensure you're using a compatible Binary Ninja version.")
raise
class MultiLineInputDialog(QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(MultiLineInputDialog, self).__init__(parent)
# Set window title
self.setWindowTitle("Variable Renaming JSON Input")
# Create layout
self.layout = QVBoxLayout()
# Add a label with instructions
self.label = QLabel("Enter JSON mapping of function addresses to variable renames (e.g., {\"0x408f3a\": {\"variables\": [{\"original_name\": \"var_18\", \"new_name\": \"digit_lower_bound\"}]}}):")
self.layout.addWidget(self.label)
# Add a multi-line text input field
self.input_field = QTextEdit()
self.input_field.setAcceptRichText(False) # Plain text only
self.input_field.setPlaceholderText(
"Example:\n"
"{\n"
" \"0x408f3a\": {\n"
" \"variables\": [\n"
" {\"original_name\": \"var_18\", \"new_name\": \"digit_lower_bound\"},\n"
" {\"original_name\": \"var_1c\", \"new_name\": \"digit_upper_bound\"}\n"
" ]\n"
" },\n"
" \"0x40bd57\": {\n"
" \"variables\": [\n"
" {\"original_name\": \"var_c_1\", \"new_name\": \"buffer_size\"}\n"
" ]\n"
" }\n"
"}"
)
self.layout.addWidget(self.input_field)
# Add OK button
self.ok_button = QPushButton("OK")
self.ok_button.clicked.connect(self.accept)
self.layout.addWidget(self.ok_button)
# Add Cancel button
self.cancel_button = QPushButton("Cancel")
self.cancel_button.clicked.connect(self.reject)
self.layout.addWidget(self.cancel_button)
# Set the layout
self.setLayout(self.layout)
# Set a reasonable size for the dialog
self.resize(600, 400)
def rename_variables_from_json(bv: BinaryView, json_input: str):
"""
Rename variables in functions within the BinaryView based on the provided JSON string.
Args:
bv: BinaryView object
json_input: JSON string containing variable renaming data
"""
try:
# Parse the JSON input
variables_dict = json.loads(json_input)
log_info("Parsed JSON input successfully:")
log_info(json.dumps(variables_dict, indent=4))
renamed_count = 0
total_vars = sum(len(data.get("variables", [])) for data in variables_dict.values())
# Log all functions in the binary for debugging
log_debug("Functions in the binary:")
for func in bv.functions:
log_debug(f"Address: 0x{hex(func.start)[2:].lower()}, Name: {func.name}")
# Normalize JSON keys by removing '0x' prefix if present
normalized_dict = {}
for addr, data in variables_dict.items():
normalized_addr = addr.lower().replace("0x", "")
normalized_dict[normalized_addr] = data
# Iterate through all functions in the binary
for func in bv.functions:
func_addr_str = hex(func.start)[2:].lower()
if func_addr_str in normalized_dict:
func_data = normalized_dict[func_addr_str]
var_list = func_data.get("variables", [])
if not var_list:
log_info(f"No variables specified for function 0x{func_addr_str}. Skipping.")
continue
log_info(f"Processing function at 0x{func_addr_str} ({func.name}) with {len(var_list)} variables to rename")
# Access variables directly (no HLIL generation here to avoid implicit analysis waits)
for var_data in var_list:
original_name = var_data.get("original_name", "")
new_name = var_data.get("new_name", "")
if not original_name or not new_name:
log_error(f"Missing original_name or new_name for function 0x{func_addr_str}. Skipping entry: {var_data}")
continue
# Find the variable by name in the function
found = False
for var in func.vars:
if var.name == original_name:
try:
# Rename the variable
var.name = new_name
renamed_count += 1
log_info(f"Renamed variable '{original_name}' to '{new_name}' in function 0x{func_addr_str}")
found = True
break
except Exception as e:
log_error(f"Error renaming variable '{original_name}' in 0x{func_addr_str}: {str(e)}")
if not found:
log_info(f"Variable '{original_name}' not found in function 0x{func_addr_str}")
# Summary of renaming operation
log_info(f"\nRenaming complete: {renamed_count} out of {total_vars} variables renamed successfully")
if renamed_count < total_vars:
log_info("Some variables were not renamed. Possible reasons:")
log_info("- Function addresses in JSON do not match any functions in the binary.")
log_info("- Variable names in JSON do not match any variables in the specified functions.")
log_info("- Check the debug log for the full list of binary functions.")
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
log_error(f"Invalid JSON input: {str(e)}")
except Exception as e:
log_error(f"Unexpected error during renaming: {str(e)}")
def ask_for_json_input(bv: BinaryView):
"""
Prompt the user for JSON input and process it to rename variables.
Args:
bv: BinaryView object
"""
# Get the UI context
ui_context = UIContext.activeContext()
if not ui_context:
log_info("Error: No active UI context found.")
return
# Create and show the dialog
dialog = MultiLineInputDialog(ui_context.mainWindow())
result = dialog.exec() # Use exec() for PySide6 compatibility
# Process the result
if result == QDialog.Accepted:
user_input = dialog.input_field.toPlainText().strip()
if user_input:
log_info("User provided JSON input:\n" + user_input)
rename_variables_from_json(bv, user_input)
else:
log_info("No input provided.")
else:
log_info("Input was canceled by the user.")
# Register the plugin
PluginCommand.register(
"Step 3. Rename Variables from JSON",
"Pops up a custom Qt dialog to input a JSON mapping for renaming variables in functions.",
ask_for_json_input
)
What’s in the Code?
- MultiLineInputDialog Class: This sets up a friendly Qt dialog box using PySide6. It’s got a text area where I can paste the JSON, complete with an example to guide me. There’s an OK button to submit and a Cancel button if I change my mind. It’s simple but does the job perfectly.
- rename_variables_from_json Function: This is the heavy lifter. It takes the JSON and the BinaryView (Binary Ninja’s way of looking at the binary), then goes through each function. If a function’s address matches the JSON, it renames the variables as specified. It’s smart about handling addresses (like ignoring “0x” prefixes) and logs everything, so I know what’s happening.
- ask_for_json_input Function: This one kicks things off by showing the dialog box. It grabs the current UI context, displays the dialog, and if I hit OK, it sends the JSON to rename_variables_from_json. If I cancel or leave it blank, it just logs that and moves on.
- Plugin Registration: The script hooks into Binary Ninja with PluginCommand.register, adding a menu option called “Step 3. Rename Variables from JSON.” It’s how I launch the whole process from Binary Ninja’s interface.
Wrapping It Up
Using AI to rename variables is a game-changer for code analysis. It takes the headache out of deciphering generic names and lets me focus on the big picture. This Binary Ninja plugin ties it all together, making it easy to apply AI’s suggestions and keep the process hassle-free. Whether you’re a reverse engineering pro or just dipping your toes in, this approach can save you time and make code way easier to understand.